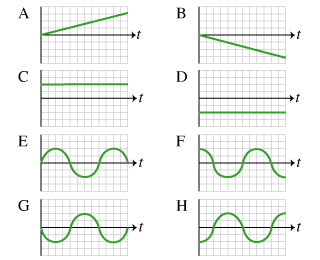
In the case. Time graph to construct a motion map.
Solved While Working On Her Bike Amanita Turns It Upside Chegg Com
Consider the position versus time graph.
. Each square unit in the horizontal axis corresponds to one second and each square unit in the vertical axis corresponds to one meter. A graph labeled velocity versus time with horizontal axis time seconds and vertical axis velocity meters per second. The vertical axis y-axis shows the velocity of the object while the horizontal axis x-axis show the time the object travels.
Position x Time t. In this graph the y-axis represents the position of the object wrt the starting point and the x-axis represents the time. Which position x versus time t graph corresponds to the motion diagram shown below.
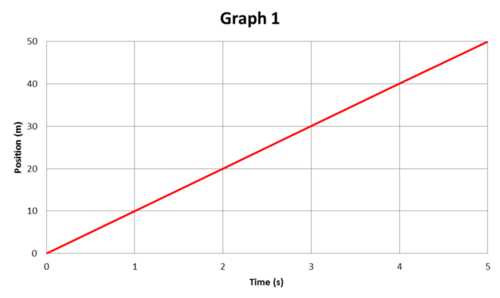
Consider the position versus time graph. A graph with horizontal axis time seconds and vertical axis position meters. A line runs straight upward from 0 seconds 0 minutes.
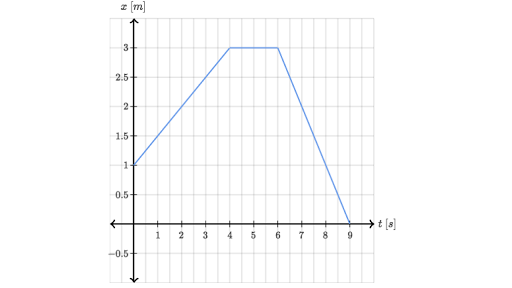
Here the object starts its motion from the origin x0 x 0 at time t0 t 0. 15 10 position m 20 time 3 What is the displacement of the particle for the entire 23 seconds. Velocity-time graph is known to be the graph that shows the velocityspeed and the direction that the object is moving over a period of time.
Just as we could use a position vs. What the average velocity the ant during the segment from D to E. 1 2 3 4 5 6t s x A B.
In the graph above the object has travelled a distance. Time the instantaneous velocity at any given point pxt on the function xt is the derivative of the function xt with respect to time at that point. Time graph of a moving particle for a time interval of 23 seconds is shown below.
Part b which of the graphs corresponds to angular. Thanks again 0 Comments. If we use a little algebra to re-arrange the equation we see that d v t.
This shows that the distance traveled by the object is directly proportional to the time taken. Graphing rotation linear quantites. These kind of graphs can also be referred to speed-time graphs.
Since the wheel is spinning at a constant speed this angle is continuously. A straight line begins at 0 seconds 10 meters per second and runs to 5 seconds 2 meters per second. The position versus time graph for an accelerating object is a parabola.
In this case to what would the slope and y-intercept refer. Other quantities such as displacement are said to depend upon it. All help is greatly appreciated.
D 40 30 20 B 10 A E 0 1 3 4 6 time O - 15 ms u uonIsod. A graph of position versus time therefore would have position on the vertical axis dependent variable and time on the horizontal axis independent variable. At the time t 1 s is the speed of A greater than less than or equal to the speed of B.
While working on her bike Amanita turns it upside down and gives the front wheel a counterclockwise spin. Correct option is A When an object travels equal distances in equal intervals of time it moves with uniform speed. The Importance of Slope.
Physics questions and answers. Position Time Graph. The graph shows a position-versus-time graph for the motion of objects A and B moving along the same axis.
The derivative of a function at any given point is simply the instantaneous rate of change of the function at that point. While working on her bike Amanita turns it upside down and gives the front wheel a counterclockwise spin. X-t x t graph the vertical axis is the position of the moving object at any instant of time relative to the starting point.
Time graph to determine velocity we can use a velocity vs. Describing the angular position The angular position of the wheel is the angle through which it has rotated since its initial orientation. The principle is that the slope of the line on a position-time graph reveals useful information about the velocity of the object.
During this portion of the motion she records the x and y positions and velocities as well as the angular position and angular velocity for the point on the rim. The graph above represents position x versus time t for an object being acted on by a constant force. Part B Which of the graphs corresponds to angular position versus time.
The position-versus-time graph shown below corresponds to an ant moving along the x-direction. Various segments of the motion are identified by the letters. In Figure 216 we have velocity on the y -axis and time along the x.
Lets look back at our original example. 1 A B 2 A B 3 A B. We know that v d t.
Time graph to determine position. Describing the x position As the wheel turns the yellow-orange dot moves in a circle around the origin. The parabola opens upward if the acceleration is positive and it opens downward if the acceleration is negative.
A As you can see from the graph at position y12 y. It spins at approximately constant speed for a few seconds. This graph shows how the position of an object changes with varying times.
Determine the initial value of the x position versus time graph At its initial location is the x position of the yellow-orange dot positive negative or zero. It spins at approximately constant speed for a few seconds. How do I create a script that will plot the vectors of time valuest and position valuesx at the same time where as the relationship between time and position is that position is equal to the natural log of time.
A B C D and E. We can represent the motion of an object using a position-time graph. Thus for uniform speed a graph of distance traveled against time is a straight line.
In physics time is usually the independent variable. The shapes of the position versus time graphs for these two basic types of motion - constant velocity motion and accelerated motion ie changing velocity - reveal an important principle. Which of the velocity versus time graphs corresponds to this position versus time graph.
The average speed during the interval between 1 s and 2 s is most nearly A 2 ms B 4 ms C 5 ms D 6 ms 7. The graph shows a position-versus-time graph for the motion of objects A and B moving along the same axis. How to use a position vs.
Learn more about velocity-time graph. In a graph of position vs. As it moves along this circular path its position with respect to the y axis changes cyclically.
During this portion of the motion she records the x and y positions and velocities as well as the angular position and angular velocity. Graph a The graph is a straight line and displacement is increasing with increasing time.

Position Vs Time Graphs Ck 12 Foundation
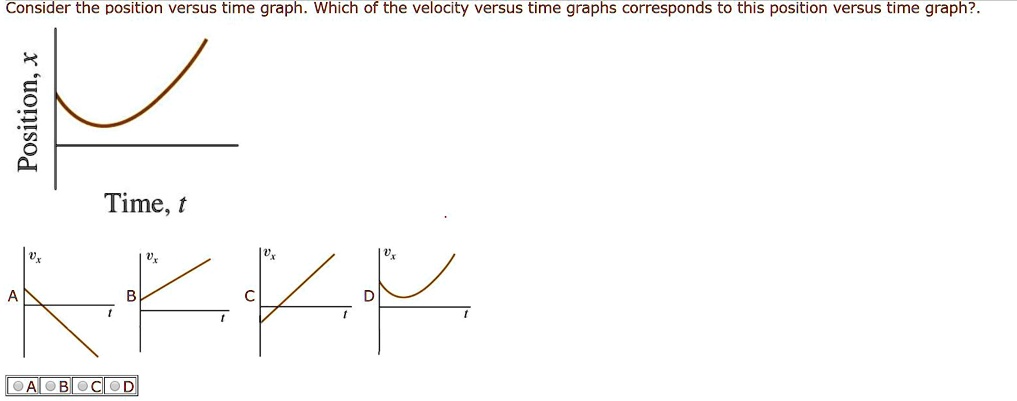
Solved Consider The Position Versus Time Graph Which Of The Velocity Versus Time Graphs Corresponds To This Position Versus Time Graph X Time
0 Comments